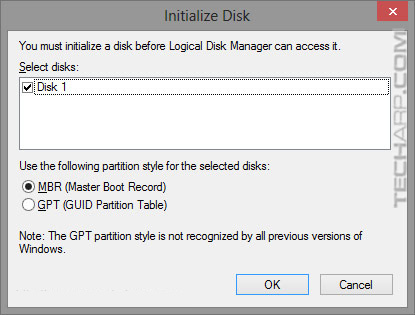
Step 4 : Use The GPT Partition Style
As advanced as the solid state drive is, it is still a storage drive to the operating system. With the exception of a few SSD-specific optimizations, it will be treated like any other drive, which means it can be partitioned and formatted like a hard disk drive. Herein lies the problem - Microsoft is extraordinarily worried about backward compatibility, which means Windows will attempt to offer you the older, outdated option even if there is a newer, better option.
When you first initialize your SSD, Windows will ask you to choose between the MBR (Master Boot Record) and the GPT (GUID Partition Table) standards for partitioning the drive. Needless to say, it defaults to MBR, so that's what most people will choose if they are not careful. To top it off, there's a note that the GPT partition style is not recognized by all previous versions of Windows. This virtually scares all but the techies who know the difference into selecting MBR.
As we wrote in our article "Should You Select MBR Or GPT When You Install A New Drive", there are only two reasons why you should ever use the decades-old MBR partitioning style :
- you intend to use the drive (now or in the future) in a system that runs Windows XP or older operating systems.
- you intend to use it as a boot drive for a 32-bit version of Microsoft Windows.
- you intend to use it as a boot drive for a 64-bit version of Microsoft Windows, but your system does not support (or has not enabled) UEFI.
For a clearer picture of what's required to support GPT in various operating systems, please take a look at the table below, or read our article "Should You Select MBR Or GPT When You Install A New Drive".
Operating Systems |
Read / Write |
Boot Support |
64-bit versions of Microsoft Windows |
||
Windows 8 |
Yes |
Yes, |
Windows XP Professional x64 Edition |
Yes |
No |
32-bit versions of Microsoft Windows |
||
Windows 8 |
Yes |
No |
Windows Server 2003 |
No |
No |
UNIX-based Operating Systems |
||
FreeBSD 7.0 (or better) |
Yes |
Yes |
Fedora 8 (or better) |
Yes |
Yes |
OS X 10.4.0 (or better) |
Yes |
Yes |
MidnightBSD 0.4 (or better) |
Yes |
Yes, |
Solaris 10 (or better) |
Yes |
Yes |
HP-UX 11.20 (or better) |
Yes |
Yes |
GPT comes with several advantages over MBR, but the most important are its more robust design. It not only uses CRC32 to ensure the integrity of the GPT header and partition tables, it has two redundant partition tables which can "self-heal" if either one gets corrupted. Unless your system or operating system does not support GPT, we highly recommend you select GPT instead of MBR.
Tech Explainer GPT was developed by Intel to overcome the limitations of MBR, which amongst other things limits the largest partition you can create to just 2 TB. Here is a list of its key benefits :
So it is very clear - GPT is far superior to MBR, and should be chosen whenever possible. For more information on GPT vs. MBR, please click here. |
| If you like this article, please share it! -> |
Step 5 : Align Your Partitions Properly
![]() Proper partition alignment is critical for optimal SSD performance and lifespan. If SSD partitions are not aligned properly, it will result in greatly reduced performance and lifespan.
Proper partition alignment is critical for optimal SSD performance and lifespan. If SSD partitions are not aligned properly, it will result in greatly reduced performance and lifespan.
Operating systems that are SSD-aware will automatically create properly aligned partitions in a solid state drive, so if you are using an SSD-aware operating system to partition and format your SSD, then you are safe.
However, if you are using an older operating system or third-party software that is not SSD-aware, like Windows XP to create and format the partitions in your SSD, then those partitions will be misaligned. Note that they will remain misaligned even if you transfer the SSD to an SSD-aware operating system like Windows 8, or install an SSD-aware operating system on it.
There are two ways to check for partition misalignment in Microsoft Windows :
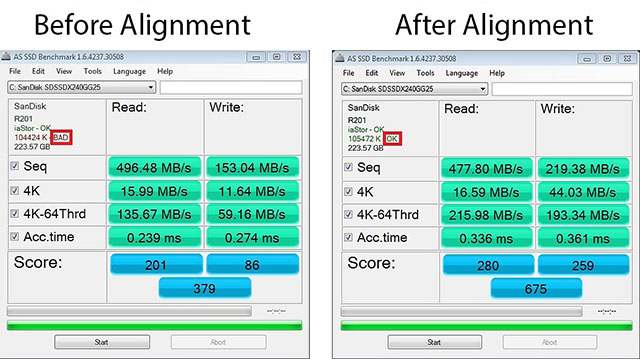
- Download and run AS SSD. This benchmark will show you if your SSD partition was misaligned with a BAD warning, as seen below.
-
Use Microsoft Windows' built-in System Information utility.
-
Run msinfo32 (either by searching for it, or going to drive:\Windows\System32).
-
Go to Components -> Storage -> Disks and look for Partition Starting Offset for your SSD.
-
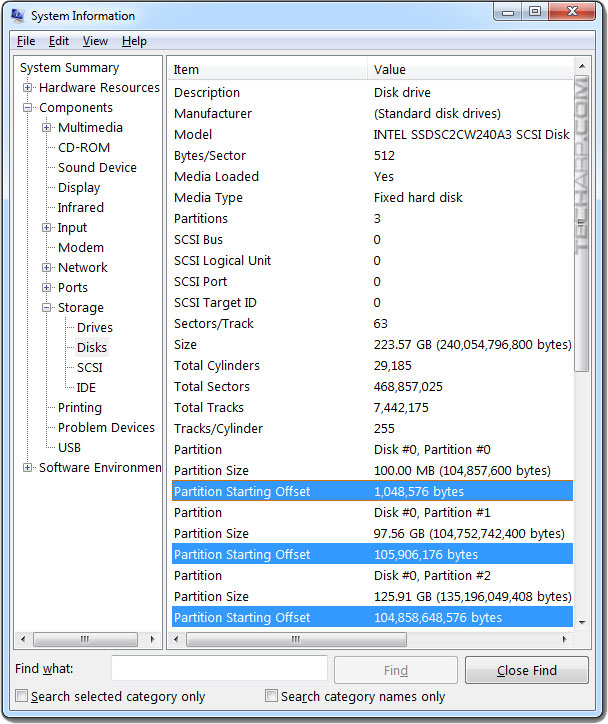
-
Use a calculator to divide each partition starting offset by 4096. If you get a whole number (no fractions!), then the partition is aligned properly.
If your SSD partitions are misaligned, you will need to redo the partitions. That means backing up your data, deleting the partitions and then creating them using an SSD-aware operating system, before formatting them and restoring your data back. Simply moving them to an SSD-aware system, or installing an SSD-aware operating system into the SSD will not work.
If you need to use your SSD with older operating systems that are not SSD-aware, you can try using third-party utilities like the WD Align utility to align the partitions for optimal performance on those operating systems.
Tech Explainer Hard disk drives have been using physical 512-byte sectors for decades, so operating systems were built around this "standard". When Windows creates the first partition in the drive, it's usually created with an offset of 63 sectors for the MBR (Master Boot Record). This does not have any alignment issues since the partition and offset were created according to 512-byte sectors. However, hard disk drives are starting to switch to the new Advanced Format technology, which uses 4 KB (4,096-byte) physical sectors to improve efficiency and increase performance. Solid state drives do not have physical sectors like hard disk drives. Instead, they have pages that are usually 4 KB in size. This new 4 KB sector or page size is exactly the same size as eight of the traditional 512-byte sectors. When these newer Advanced Format hard disk drives and SSDs are used with older Windowss operating systems that only understand the 512-byte sector, they are often partitioned with the wrong amount of offset - 63 x 512-byte sectors, which is one sector shy of 64 x 512-byte sectors, which would have allowed for perfect alignment with the new 4 KB sector / page : 64 x 512-byte sectors is exactly equivalent to 8 x 4,096-byte sectors Because of this misalignment of the initial partition's offset, all logical sectors thereafter are therefore misaligned, forcing a read-modify-write cycle for every write operation. This greatly reduces the drive's performance because the drive now has to read the contents of two 4 KB sectors before writing them back. That's twice the work for the same result. This problem is amplified in SSDs because they don't read and write in 4 KB pages, but in large blocks of multiple pages - usually 512 KB blocks (128 x 4 KB). So partition misalignment could result in the read-modify-write cycle for two 512 KB blocks if the desired data straddles across two blocks. This would result in the read, erasure and writing of 256 pages, greatly reducing the performance and lifespan of the flash memory cells. |
| If you like this article, please share it! -> |
Support Tech ARP!
If you like our work, you can help support out work by visiting our sponsors, participate in the Tech ARP Forums, or even donate to our fund. Any help you can render is greatly appreciated!
<<< How To Optimize Your SSD : Steps 1 - 3 : Previous Page | Next Page : How To Optimize Your SSD : Steps 6 - 7 >>>
Support us by buying from Amazon.com! |
|
| Grab a FREE 30-day trial of Amazon Prime for free shipping, instant access to 40,000 movies and TV episodes and the Kindle Owners' Lending Library! | |







 Add to Reddit
Add to Reddit