Tier 1 : Operating System / Kernel
When it comes to the daily operation of a PC, the operating system is the boss and calls all the shots. In the case of modern operating systems, nothing can run without its permission. In fact, from Windows 98 onwards, code must be passed to the operating system for execution, instead of being executed without its intervention.
But the reality of the situation is a bit different. The operating system acts more like a watchman. Anyone who wants to enter the building has to pass by the watchman. Unfortunately, what the watchman cannot protect against the tunnel under his feet, the open sky above his head and a grappling hook over the walls. Those entry points represent holes in the PC's security due to bugs or loopholes in the operating system.
Patches act like fixes to those holes, patching potential entry points that circumvent the usual system checkpoints. So how do you update your operating system? Well, before you get down to it, there are actually two things to update here - drivers and the actual operating system.
First, let's talk about drivers. Generally, drivers can be considered the interface to the firmware inside the device. So, if a driver has a problem or vulnerability, it could give you a big headache. Fortunately, most network devices aren't driver-based, but rather firmware-based. So, we won't be touching much on it. Let's move on to the operating system, the biggest culprit when it comes to compromised security.
A simple example of an operating system's vulnerability would be the DCOM (Distributed Component Object Model) and RPC vulnerabilities that were highlighted some time back in most versions of the Microsoft Windows operating system. RPC is generally a simple way of allowing a programmer to run code on a remote machine, while DCOM is the service that facilitates the communication between the two computers.
It seems that by using the both RPC and DCOM, hackers can execute malicious code on a remote computer. By using these twin vulnerabilities, an attacker could execute a buffer overflow attack. That is essentially running code that uses up more space than the buffer has. The new code therefore overwrites older entries in the memory buffer, and once it's in the memory buffer and past the operating system, nothing can stop it. It executes its code payload and your PC will do whatever it wants your PC to do.
 |
So, how does a patch prevent all this? Well, both services can be patched so that the operating system can keep an eye on the code that both services send to it for execution.
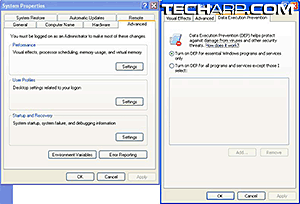
Service Pack 2 for Windows XP also comes with another patch for this problem. It allows the operating system to work in tandem with processors equipped with the NX (No Execute) or XD (Execute Disable) bit to prevent the running of code that utilizes the buffer overflow trick to run itself on a system. This feature is called DEP (Date Execution Prevention).
Now, do you see why it is important to keep your operating system updated? If you are not sure how to go about it, I'll teach you how to do it in Windows XP right now. Really, this has to be one of the easiest tutorials I've ever given. Take a look.
Step 1 : Click the Start button and go to All Programs.
Step 2 : Look to the top of the list for Windows Update and click it. An Internet Explorer window will open up and load the page.
Step 3 : Follow the instruction on screen. Windows Update will scan your computer and present you with a list of updates. Download them and let Windows Update install them.
Step 4 : Reboot and enjoy your more secure computer!
Now, wasn't that easy? Click a few buttons here and there and hey presto, you're done!







 Add to Reddit
Add to Reddit
