The Intel P55 Express
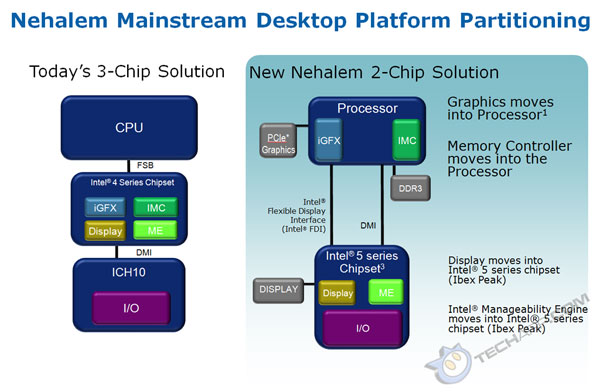
Codenamed Ibex Peak, the new Intel P55 Express marks a new level of chipset integration. Unlike older chipsets (including the new Intel X58 Express chipset), the Intel P55 Express is a single-chip solution. Intel now calls it a PCH or Platform Controller Hub. Take a look at this comparison which shows the difference between the Intel 5-series chipset and the older Intel 4-series chipset.
The I/O functions, previously handled by the Intel I/O Controller Hub (ICH) chip, is now part of the P55 Express chip, together with the display controller and the Intel Manageability Engine. The memory controller and graphics controller were shifted out of the chipset and integrated into the processor itself. So, unlike the Core i7 processor, the Lynnfield/Havendale processor is directly linked to the PCI Express graphics card.
Below is a comparison of the links between the three Nehalem-based desktop processors (the Core i7, Lynnfield and Havendale) and their chipsets and other components.
The first thing you should be aware of is that while the X58 Express uses the new Intel QPI (QuickPath Interconnect) to communicate with the Core i7 processor, the P55 Express will only use the slower DMI (Direct Media Interface) to communicate with the Lynnfield/Havendale processor. The X58 Express also uses the DMI but only for communications between the X58 Express and the ICH10.
The Intel P55 Express will also feature the Intel Flexible Display Interface (FDI) which is used to channel display data from the Havendale's integrated graphics core to the PCH's display controller. Initial steppings of the P55 Express may not have this interface working properly so they may not support the Havendale processor when it's eventually launched. The Lynnfield processor does not need this interface as it does not have an integrated graphics core.
To further differentiate the two chipsets, the X58 Express supports two PCI Express x16 slots (or four x8 slots) while the Lynnfield processor supports one x16 slot (or two x8 slots). The Havendale processor, on the other hand, only supports a single x16 slot.
Support Tech ARP!
If you like our work, you can help support out work by visiting our sponsors, participate in the Tech ARP Forums, or even donate to our fund. Any help you can render is greatly appreciated!
Page |
Topic |
1. |
|
2. |
Questions & Comments
If you have a question or comment about this article, please feel free to post them here!
| Date | Revision | Revision History |
29-10-2008 |
1.0 |
Initial Release. |







 Add to Reddit
Add to Reddit