The Solid State Drive Optimization Guide
![]() Solid state drives are fast replacing hard disk drives as the storage medium of choice, not only in notebooks but also in desktops where they serve as boot drives. They offer a tremendous performance advantage over hard disk drives, especially in random accesses. This is because solid state drives are not affected by the spatial locality of the data it accesses - data is accessed everywhere at the same speed.
Solid state drives are fast replacing hard disk drives as the storage medium of choice, not only in notebooks but also in desktops where they serve as boot drives. They offer a tremendous performance advantage over hard disk drives, especially in random accesses. This is because solid state drives are not affected by the spatial locality of the data it accesses - data is accessed everywhere at the same speed.
Hard disk drives, on the other hand, perform poorly at random accesses because they requires the read/write heads to switch between different locations - an action that takes ages (in relative terms) to perform. That's why hard disk drive manufacturers come up with faster spinning drives to reduce the amount of time it takes for the read/write heads to seek from one random bit of data to another random bit of data.
Of course, this doesn't spell the end of the ubiquitous hard disk drive. In fact, the hard disk drive is expected to soldier on for the next few decades thanks to the industry's ability to continuously innovate to keep ahead of the curve. Until solid state drives can deliver the hard disk drive's ultra-low cost per MB and cavernous storage capacity, the hard disk drive is here to stay.
The solid state drive itself also has issues that preclude its ascendency over the hard disk drives. Its flash memory cells have a limited lifespan, which is set to get worse as their fabrication process shrinks. They can also perform badly under certain circumstances which result in a dearth of "clean" blocks to write to. This is because the flash memory cells in SSDs can only be written to if they are empty. Cells that contain data (even useless, deleted data) must be erased before any new data can be written to it. This requires the SSD to perform the time-consuming read-erase-modify-write cycle to overwrite the "dirty" block, which not only cripples performance but also increases wear on the affected memory cells.
Modern SSDs use a mix of techniques and technologies like overprovisioning of memory cells, wear levelling, a write combine buffer (or on-the-fly data compression), and the Trim command or automatic garbage collection to maintain performance and extend the lifespan of the flash memory cells. However, there's only so much they can do.
This is where the Solid State Drive Optimization Guide comes in. In this guide, we will show you how to maintain the performance and longevity of your solid surface drive. You will note that in most cases, they both go hand-in-hand - maximizing your SSD's performance often results in longer lifespan of the flash memory cells, and vice versa. Let's get right down to it.
| If you like this article, please share it! -> |
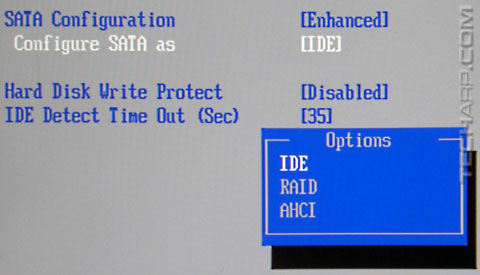
Step 1 : Enable AHCI / RAID Mode
You should check the BIOS and make sure that the SATA controller is set to the AHCI or RAID modes. This is important as many motherboards still default to the IDE (or Legacy) mode for the SATA controller.
Switching from IDE to AHCI or RAID modes will enable NCQ (Native Command Queuing) for the SATA controller. This allows the SATA controller to queue and rearrange up to 32 outstanding read or write commands.
|
This feature will improve the performance of all SATA devices in the computer, including your SSD, by optimizing the sequence in which those commands are carried out.
Enabling the AHCI or RAID mode will also enable support for the Trim command which helps to keep your SSD performing optimally, although Windows 7 and Windows 8 native drivers will support the Trim command even in legacy IDE mode.
Please see the Tech Explainer in Step 7 : Verify That Trim Is Enabled for more information on the Trim command.
Warning! It's best to enable AHCI / RAID mode before installing Windows. If you switch from IDE to AHCI / RAID after Windows is installed, it will result in a Blue Screen Of Death (BSOD) with the error message "STOP 0x0000007B INACCESSABLE_BOOT_DEVICE" when you attempt to boot up. You can fix this problem by following the steps in this Microsoft Knowledge Base article. We recommend you read it before making the switch. In the worst case scenario, you can always go back to the BIOS and revert to IDE / Legacy Mode. This will allow you to boot into Windows again. |
| If you like this article, please share it! -> |
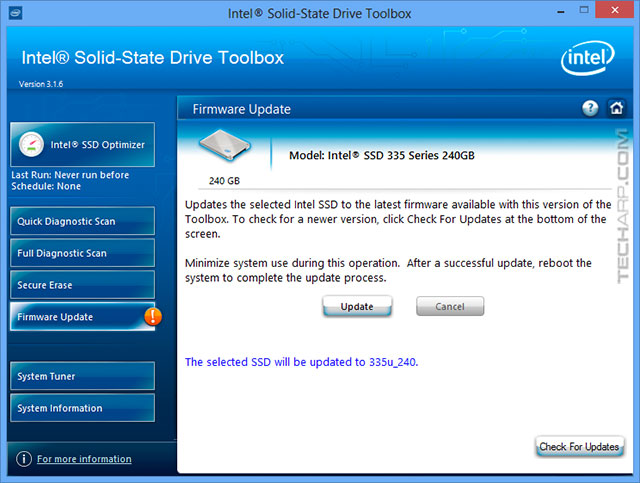
Step 2 : Update Your SSD Firmware
Check with your SSD manufacturer if they have a firmware update for your SSD. Whenever possible, you should ensure that your SSD has the latest firmware, because they often fix bugs and improve performance.
This is particularly important for lower-end drives and smaller manufacturers, because their emphasis would be to get the SSDs out into the market as soon as possible, even if there are still some bugs to be ironed out, or their performance have yet to be optimized.
|
Warning! Updating the firmware of some SSDs may require the complete wiping of the drive contents, so please CAREFULLY READ the warnings and instructions of the firmware update before you proceed. |
| If you like this article, please share it! -> |
Step 3 : Upgrade Your Operating System
Solid state drives perform best with operating systems that are not only SSD-aware but also optimized for their operation. This not only includes support for Trim operations and proper partition alignment, but also the disabling of certain HDD-specific optimizations like Superfetch, ReadyBoost and Prefetching in Windows 7 and Windows 8.
Therefore, if you are upgrading to an SSD, it's best to upgrade your operating system as well, if it is not at least SSD-aware. Here's a list of operating system versions that are SSD-aware :
Operating System |
SSD-Aware Version |
Notes |
Microsoft Windows 8 |
All versions |
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 |
All versions |
|
Microsoft Windows 7 |
All versions |
Trim is only supported for SATA SSDs, but not PCIe SSDs. |
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 |
All versions |
Trim is only supported for SATA SSDs, but not PCIe SSDs. |
Microsoft Windows Vista |
All versions |
Aligns SSD partitions properly, but does not support Trim. |
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 |
All versions |
Aligns SSD partitions properly, but does not support Trim. |
Mac OS X |
10.6.8 onwards |
Trim is possibly supported only in Apple SSDs, with third-party utilities required to enable it for other SSDs. |
Linux |
2.6.33 onwards |
Disabled by default, and must be enabled by setting the "discard" mount option. |
FreeBSD |
8.3 onwards |
|
To ensure that your SSD is properly set-up, it's advisable to fresh install the operating system on it. Otherwise, use a desktop with an SSD-aware operating system to prepare it by partitioning and formatting in advanced. This ensures that the SSD will be partitioned properly
| If you like this article, please share it! -> |
Support Tech ARP!
If you like our work, you can help support out work by visiting our sponsors, participate in the Tech ARP Forums, or even donate to our fund. Any help you can render is greatly appreciated!
Support us by buying from Amazon.com! |
|
| Grab a FREE 30-day trial of Amazon Prime for free shipping, instant access to 40,000 movies and TV episodes and the Kindle Owners' Lending Library! | |







 Add to Reddit
Add to Reddit