The RAM Disk Guide
A RAM disk (also known as RAM drive or virtual RAM drive) turns RAM into a logical disk drive for temporary storage purposes. It can come in the form of a software that converts a portion of regular computer memory into a drive, or an actual physical device that uses RAM as a storage medium. Both offer a tremendous boost in storage speeds of several magnitudes over the hard disk drive.
The RAM disk has been around since the 1980s, but it has never been popular due to the high cost of computer memory. It is now making a comeback, partly because RAM is now cheap and plentiful and partly because solid state drives (SSDs) are fast replacing hard disk drives as the storage medium of choice, not only in notebooks but also in desktops where they serve as boot drives.
SSDs are not only much faster than hard disk drives, they are silent and virtually impervious to vibration and shock. The downside though is their limited lifespan, especially consumer-grade SSDs which use MLC flash memory that last only 5,000 program/erase cycles. That's where the RAM disk comes in - it allows the user to reduce wear and tear on the SSD by shifting some of the work to it.
There are, of course, pros and cons to the RAM disk, and this guide will guide you through it all. On top of that, we will teach you how to make full use of your RAM disk. Let's get right down to it!
Why Use A RAM Disk?
Here are a couple of reasons why you should use a RAM disk :
 |
-
Speed - A RAM disk uses RAM as its storage medium, so it is very, very fast. The average DDR3-1600 memory is 30-40x faster than typical desktop SSDs and more than 60x faster than the fastest desktop hard disk drive (the 1 TB Western Digital VelociRaptor). It also does not suffer any performance penalty from data fragmentation, or random accesses.
It also allows you to eliminate the higher latencies associated with the hard disk drive or even the SSD when you are benchmarking the transfer rate of high-speed storage media, like the 256 GB Kingston UHS-I SDXC Card.
-
Reduces bottleneck - A RAM disk runs off the much faster memory interface, instead of the slower SATA interface. Offloading part of the workload to a RAM disk therefore reduces the load on the SATA interface, allowing more operations to occur simultaneously.
-
Auto-clearing - Data in a RAM disk is automatically cleared every time the computer shuts down, or whenever the RAM disk is restarted. If used to store temporary files used by the operating system and applications, they would be automatically deleted instead of accumulating and wasting space as they do on regulars drives.
-
Security - Data stored in a RAM disk are irrevocably lost whenever the computer or the RAM disk restarts, because RAM cannot retain data for more than a second or so without power. This is extremely useful for temporarily storing sensitive data. When combined with a secure operating system login, it has the added benefit of securely wiping out said sensitive data if your computer is stolen or tampered with.
-
No lifespan issues - Unlike the NAND flash memory used in SSDs, RAM has no wear and tear issues. It won't wear out even if you use it at full load 24/7. RAM disks are therefore extremely suitable for high-intensity read/write operations.
- Maintain your SSD's performance and lifespan - By shifting temporary file storage and caching to the RAM disk, this not only reduces the wear and tear load on the SSD, but it also helps to maintain the SSD's performance over time.
When Should You NOT Use A RAM Disk?
On the other hand, there are circumstances where a RAM disk should never be used :
-
Not enough RAM - This is subjective and depends on your usage. Most users get by with 4 GB of RAM although some can't live without 8 GB or even 16 GB of RAM. Generally, we do not recommend that you use a RAM disk unless you have at least 6 GB of RAM.
-
To place a paging file - Although it is possible to do so, placing the paging file on a RAM disk is absurd because it would be like transferring water from one storage tank to another and then back again. The only reason why an application would need to use a paging file is because it doesn't have enough RAM, and if that's because you allocated too much of it (see Not enough RAM above) to the RAM disk, you are only exacerbating the problem.
-
The data is important - To the operating system, a RAM disk is no different from any other drive. You can partition it, format it and perform any kind of file operations on it. However, it is NOT a permanent storage medium, so you should never store your documents on it. Any data that is stored on a RAM disk is permanently lost if the computer crashes, shuts down or restarts.
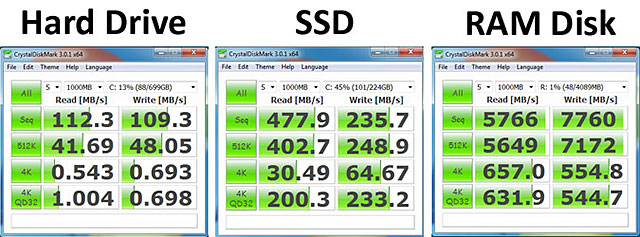
How Fast Is A RAM Disk Really?
Avram Piltch, from Laptop, compared the performance of a 4 GB RAM disk versus a 7,200 RPM hard disk drive and a Kingston HyperX SH100S3 SSD. Check out just how much faster the RAM disk was, compared to the HDD and the SSD.
The RAM Disk is faster than the... |
HDD |
SSD |
|
1 MB Sequential Reads |
51.3x |
12.1x |
|
1 MB Sequential Writes |
71.0x |
32.9x |
|
512 KB Random Reads |
135.5x |
14.0x |
|
512 KB Random Writes |
149.3x |
28.8x |
|
4 KB Random Reads |
1210x |
21.5x |
|
4 KB Random Writes |
800.6x |
8.6x |
|
4 KB Random Reads |
629.4x |
3.2x |
|
4 KB Random Writes |
780.4x |
2.3x |
This is the reason why we use a RAM disk for our copy and write tests, whether it's for external hard disk drives like the 2 TB WD My Passport Pro, or flash memory media like the 256 GB Kingston UHS-I SDXC Card. Even if we use a very fast hard disk drive, like the 1 TB Western Digital VelociRaptor, the results would be skewed by the fact that it takes the computer some time to read from or write to the hard disk drive.
This can be reduced by using an SSD, but even an SSD cannot match a RAM disk in delivering ultra-high throughput to minimise the latencies that would skew the benchmark results.
| If you like this article, please share it! -> |
Support Tech ARP!
If you like our work, you can help support out work by visiting our sponsors, participate in the Tech ARP Forums, or even donate to our fund. Any help you can render is greatly appreciated!
Page |
The RAM Disk Guide |
|
1 |
• Why Use A RAM Disk? |
|
2 |
||
3 |
||
4 |
||
5 |
||
6 |
||
7 |
||
8 |
Support us by buying from Amazon.com! |
|
| Grab a FREE 30-day trial of Amazon Prime for free shipping, instant access to 40,000 movies and TV episodes and the Kindle Owners' Lending Library! | |







 Add to Reddit
Add to Reddit