Introduction
Computer performance have increased at an amazing rate in recent years, and unfortunately so does power consumption. An ultimate gaming system equipped with a quad-core processor, two NVIDIA GeForce 8800 Ultra, 4 sticks of DDR2 memory and a few hard drives can easily consume 200W without doing anything! To reduce power wastage, a few industry standards have been developed to make our computers work more efficiently.
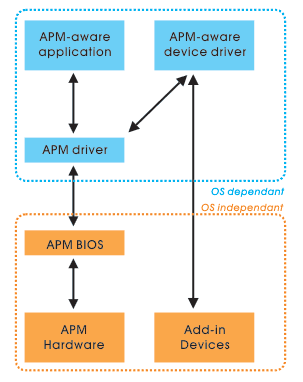
In January 1992, Intel and Microsoft developed APM (Advanced Power Management) to manage power when a computer system is idling. Later in December 1996, the successor of APM – the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) specification was developed by Compaq, Microsoft, Intel, Phoenix and Toshiba as the industry open-standard power management interface. What's the difference? Let's take a look :
|
In this article, I will not go into APM as most PC use ACPI these days.
Sections |
Topics |
|
ACPI Power Management States |
||
Global System States (G-States) |
G0
Working States |
|
Sleeping States (S-States) |
||
Device States (D-States) |
||
CPU Power States (C-States) |
||
CPU / Device Performance States (P-States) |
||
C-States
In Multi-Core Processors |
||
Other
P-State Features |
||
Conclusion |







 Add to Reddit
Add to Reddit